Introduction:
Paranoid schizophrenia is a chronic mental health condition that falls under the spectrum of schizophrenia disorders. Characterized by paranoia and delusional thinking, this condition can significantly impact an individual’s perception of reality, relationships, and overall quality of life. Understanding its symptoms, potential causes, and treatment options is crucial for those living with the condition and their loved ones.

What is Paranoid Schizophrenia?
Paranoid schizophrenia is one of the subtypes of schizophrenia, primarily defined by the presence of paranoia and auditory hallucinations. While other types of schizophrenia may cause disorganized thinking or catatonic behavior, paranoid schizophrenia predominantly involves false beliefs that others intend harm or are plotting against the individual.
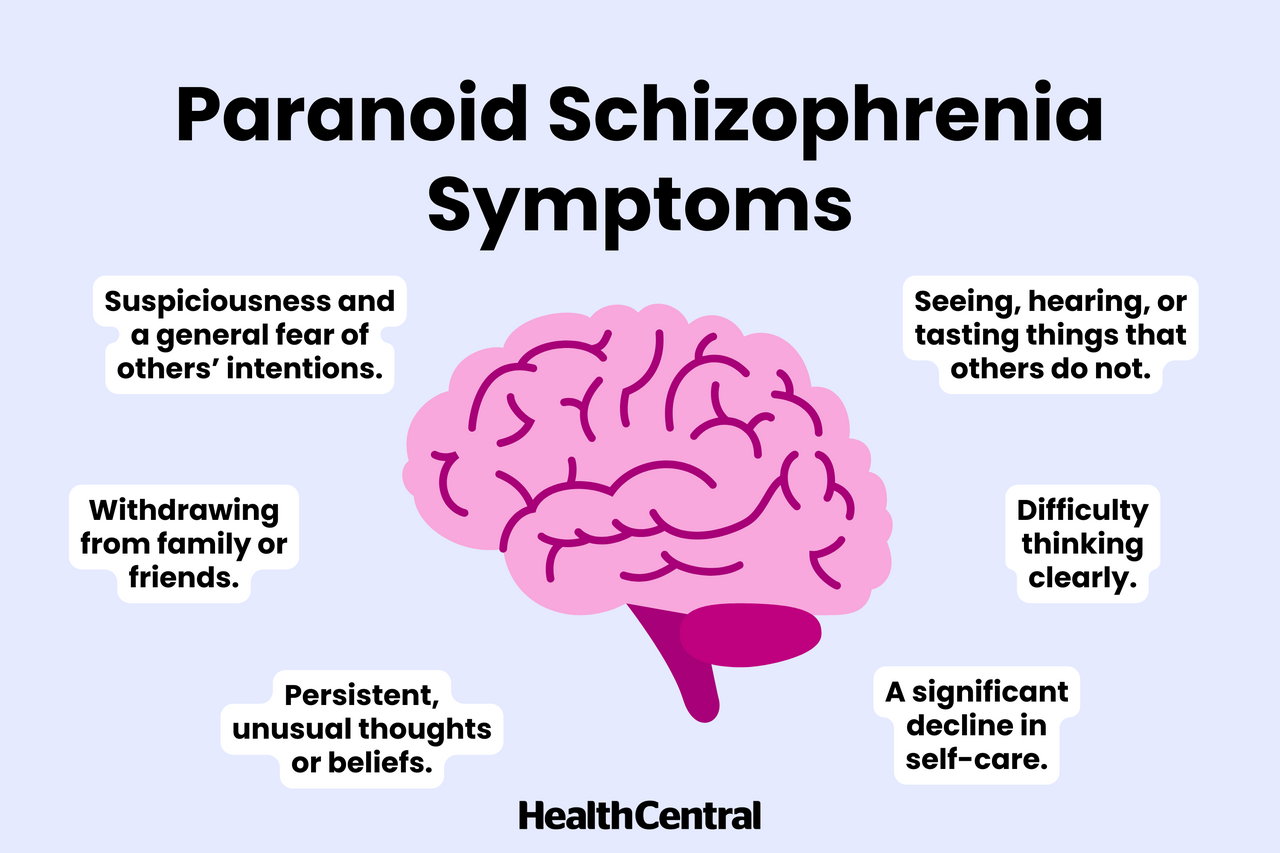
Key Symptoms:
1. Delusions of Persecution:
Believing others are conspiring against, spying on, or planning to harm them.
2. Auditory Hallucinations:
Hearing voices that others cannot hear, often critical or commanding in nature.
3. Heightened Suspicion:
Distrust of friends, family, or even strangers, leading to social isolation.
4. Difficulty in Reasoning:
Struggling to differentiate between reality and delusional beliefs.
5. Emotional Dysregulation:
Experiencing anxiety, anger, or fear stemming from perceived threats.
Potential Causes:
The exact cause of paranoid schizophrenia remains unclear, but several factors may contribute:
1. Genetics:
A family history of schizophrenia increases the risk.
2. Brain Structure and Chemistry:
Imbalances in brain chemicals like dopamine and serotonin, or structural abnormalities, can influence symptoms.
3. Environmental Factors:
Trauma, stress, or exposure to viruses or malnutrition during fetal development may play a role.
4. Substance Use:
Misuse of drugs like cannabis, LSD, or amphetamines can trigger or worsen symptoms
Diagnosis and Challenges:
Diagnosing paranoid schizophrenia involves a comprehensive evaluation, including:
– Medical history and physical exams.
– Psychiatric assessments to identify delusions or hallucinations.
– Imaging tests to rule out other medical conditions.
One major challenge is that individuals with the condition often lack insight into their illness, making treatment acceptance difficult.
Treatment Options:
1. Medication:
Antipsychotics:
Medications like risperidone or olanzapine help manage hallucinations and delusions.
Mood Stabilizers:
Used to address emotional dysregulation.
2. Psychotherapy:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
Helps patients identify and challenge delusional thoughts.
Family Therapy:
Educates families on supporting their loved one and managing challenges.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments:
– Maintaining a structured routine, regular exercise, and proper nutrition can enhance overall well-being.
4. Support Groups:
– Connecting with others facing similar challenges can reduce isolation and provide coping strategies.
Living with Paranoid Schizophrenia:
With early intervention, appropriate treatment, and consistent support, many individuals with paranoid schizophrenia can lead fulfilling lives. Building a strong support network and fostering open communication with mental health professionals is essential.
Conclusion:
Paranoid schizophrenia is a complex condition requiring empathy, understanding, and multidisciplinary care. Raising awareness about the disorder can help combat stigma and ensure that individuals receive the support they need to thrive.





